CAA News Today
CAA 2021: A look back on the past year’s programming, publications, and opportunities
posted by CAA — November 30, 2021
CAA has produced this reel with a compilation of events, scholarship, programs, and initiatives CAA from the last year. See below for a full list of each item (in order of appearance in the video) with links to learn more.
Programming:
CAA’s first virtual Annual Conference
Mariam Ghani in conversation with Laura Anderson Barbata
In Conversation with Dr. Nancy Odegaard
Theresa Avila, Annual Conference Program Chair in conversation with Meme Omogbai
An Inaugural Evening with CAA Distinguished Awardees and Artists
CAA Then & Now: Reflections on the Centennial Book and the Next Century
Karen Leader, author of Chapter 12: Advocacy
Opportunities:
Publication, travel, and support grants
Publications and Publications Programming:
Artist Project, Elana Mann for Art Journal Open
Roundtable discussion for Art Journal Open, Holding Space…
Art Journal and The Art Bulletin
caa.reviews book and exhibition reviews
caa.reviews’s dissertation roster, 2020
Global Programs
CAA-Getty International Program
CAA-Getty 10-Year International Program online publication
Podcasts
CAA Conversations by CAA’s Education Committee
CAA’s 110th Annual Conference will take place in Chicago from February 17-19, followed by virtual live sessions to be held in Zoom from March 3-5. For more information and to register go to this link.
An Interview with Nicole Archer, Editor-in-Chief of Art Journal Open
posted by CAA — June 15, 2020

Nicole Archer.
We’re delighted to introduce readers to Nicole Archer, the current Editor-in-Chief of Art Journal Open (AJO), CAA’s online forum for the visual arts that presents artists’ projects, conversations and interviews, scholarly essays, and other forms of content from across the cultural field. Founded in 2012 as an open-access affiliate of Art Journal, Art Journal Open has been independently edited since 2014. It remains open access and is always free to explore.
Nicole Archer researches contemporary art and design, with an emphasis in textile and garment histories. She is an Assistant Professor in the Department of Art and Design at Montclair State University, where she extends this research through a teaching practice that encourages students to explore politics and aesthetics via close examinations of style, embodiment, and desire.
Amidst the end of the academic year, we corresponded with her over email to learn more about her research, her thoughts on the impact of COVID-19, and her aspirations for Art Journal Open.
Where are you from originally?
I was born in Brooklyn and raised mainly in South Florida, but I spent most of my adult life in San Francisco. In 2018, I returned to New York City.
What pathways led you to the work you do now?
My path has been shaped by a long line of committed feminist art historians, theorists, and activists who have inspired me to pursue work that is wildly curious, ethically responsible, and politically committed to issues of social justice. This, coupled with the fact that I started my college career in the mid-1990s, when the field of Visual Studies was demanding that Art History be held accountable for the role it played in supporting certain cultural hegemonies. It was a time when we were recognizing the benefit that many art historical methods could bring to critical cultural studies (and vice versa).
When did you first become a CAA member?
I have been a CAA member since 2011, but I was an avid reader of Art Journal and The Art Bulletin long before that (thanks to my library access).
What are you working on or thinking about currently?
I am currently finishing a book manuscript that considers how textiles (our key mediums of comfort and security) have been strategically manipulated over the last two decades to aid in the systematic reshaping of what constitutes “legitimate” versus “illegitimate” forms of state violence. The book tells interwoven, materially grounded stories regarding global arts and design practice, on the one hand, and military, police, and governmental action, on the other, to theorize how feelings of insecurity are produced, aesthetically.
What are your thoughts on the impact of COVID-19 on the work you do? On the field?
I think the current pandemic makes two things particularly clear. First, it highlights the important role that art and design can play in helping a society understand (and bear) emergent and acutely difficult circumstances. From movie marathons, artist talks, and book readings that we have enjoyed during our nights spent ‘sheltering in place,’ to the protest banners, photographs, and balcony performances that have led our communities towards acts of collective care and solidarity with one another.
Second, COVID-19 puts the varied inequities that underwrite the field in high relief. It makes the economic precarity of so many cultural workers glaringly obvious, and it forces us to recognize how undervalued cultural work actually is. We need to ask why we have allowed the arts to become so defunded and privatized (despite the social value it clearly delivers). Calls for austerity are circulating, and we know this means further cuts to already underfunded public arts initiatives. We need to resist this and seize this moment as an opportunity to insist on our value. We need to stop undercutting ourselves and our peers, and refuse to accept the exploitation of adjunct professors and graduate student teachers. We must do this as we push against the increasingly prohibitive costs of arts education.
 What led you to be interested in working on Art Journal Open?
What led you to be interested in working on Art Journal Open?
It is our shared responsibility, as arts and design professionals, to constantly “check” our field of practice—to find time to celebrate what we are doing well, and to redress and learn from our shortcomings. I believe this responsibility is a cornerstone of AJO’s editorial mission. Working on AJO is a unique opportunity to hold myself, and others, accountable on this front.
What is your vision for Art Journal Open during your tenure?
I hope to build on the solid foundation laid by the journal’s previous editors, and to further emphasize the open dimension of the publication’s identity—to treat “Open” as a verb, a call to action. We hope to accomplish this by leveraging the journal’s digital format, to open space for more multi-media Creative Projects, and to take advantage of our lack-of-paywall to help draw new readers to AJO and new voices to CAA.
The first three pieces published after Nicole Archer fully took over as Editor-in-Chief of Art Journal Open.
What would you say is your top arts-related recommendation (book, website, resource) at the moment?
I know I am late to this, but I recently found an online radio station called NTS and it is giving me life! I miss trusting my night to a DJ, hearing a new song out of nowhere, and dancing with strangers. I am also tired of soundscapes controlled by algorithms. People should give it a listen in their studios and kitchens, and at their computers and writing desks.
View this post on Instagram
A favorite artwork?
Last year, I had the opportunity to see Sonya Clark’s Monumental Cloth, The Flag We Should Know at the Fabric Workshop and Museum in Philadelphia, and I have not been able to stop thinking about it since. Clark’s work epitomizes the important role art can play in ensuring that political discourse maintains its complexity in the face of a mediascape set on transforming these conversations into flat lines in the sand.
At the center of the exhibit was a monumental replica (15’x30’) of a white dish towel waived by Confederate troops in April 1865, before General E. Lee negotiated the terms of the Confederacy’s surrender. Displayed in a manner akin to the Star Spangled Banner (a centerpiece of the Smithsonian National Museum of American History’s collection), Monumental Cloth presented the Confederate Truce Flag as testament to a decisive moment in US history. It demanded that we ask why we do not know this flag, as a means to discuss anti-Blackness and the persistence of white supremacy in the United States. It provided a poignant, aesthetic counterstrategy to other manners of “memorializing” the Confederacy. The exhibit offered spaces of contemplation alongside opportunities for direct action—by setting-up looms that visitors could use to weave additional Truce Flag replicas, in opposition to the endless flow of commercially produced items made to bear the image of the Confederate Battle Flag.
What are you looking forward to?
Honestly, I am looking forward to the end of the Trump presidency, and to the possibility that the moment we are in could force real political and cultural change; that conversations around universal basic income and healthcare will gain traction, and that widespread recognition of the systemic racism inherent in the criminal justice system will open the door to both abolishing the prison system and defunding and demilitarizing the police that tyrannize communities of color in the US.
NICOLE ARCHER BIOGRAPHY
Nicole Archer researches contemporary art and design, with an emphasis in textile and garment histories. She is an Assistant Professor in the Department of Art and Design at Montclair State University, where she extends this research through a teaching practice that encourages students to explore politics and aesthetics via close examinations of style, embodiment, and desire.
Her work has been published in various journals, edited collections, and arts publications, including: Criticism: A Quarterly Journal for Literature and the Arts; Textile: The Journal of Cloth and Culture; Trap Door: Trans Cultural Production and the Politics of Visibility (published by the New Museum + MIT Press); Where are the Tiny Revolts? (published by the CCA Wattis Institute for Contemporary Arts + Sternberg Press); Women and Performance: A Journal of Feminist Theory.
An Interview with Suzanne Preston Blier on CAA’s Code of Best Practices and Publishing with Fair Use
posted by CAA — May 19, 2020
 In 2019, Suzanne Preston Blier, professor of African art at Harvard University and former president of CAA, published a major book on Picasso’s use of global imagery, Picasso’s Demoiselles: The Untold Origins of a Modern Masterpiece. In addition to its scholarship the book is groundbreaking for its reliance on fair use, the principle within US copyright law that permits free reproduction of copyrighted images under certain conditions. CAA led the way among visual arts groups in calling for reliance on fair use, producing in 2015 its Code of Best Practices in Fair Use for the Visual Arts.
In 2019, Suzanne Preston Blier, professor of African art at Harvard University and former president of CAA, published a major book on Picasso’s use of global imagery, Picasso’s Demoiselles: The Untold Origins of a Modern Masterpiece. In addition to its scholarship the book is groundbreaking for its reliance on fair use, the principle within US copyright law that permits free reproduction of copyrighted images under certain conditions. CAA led the way among visual arts groups in calling for reliance on fair use, producing in 2015 its Code of Best Practices in Fair Use for the Visual Arts.
In this interview with Patricia Aufderheide, university professor and founding director of the Center for Media & Social Impact (CMSI) at American University, and a principal investigator in the CAA fair use project, Blier relates how she became an inadvertent pioneer of fair use in art history.
An Interview with Suzanne Preston Blier, Harvard University
By Patricia Aufderheide, American University
I met Prof. Blier, an award-winning art historian, when CMSI joined others in facilitating the Code of Best Practices in Fair Use for the Visual Arts for the College Art Association (CAA), with funding from the Samuel H. Kress and Andrew W. Mellon Foundations. Fair use is the well-established US right to use copyrighted material for free, if you are using that material for a different purpose (such as academic analysis, for instance) and in amounts relevant to the new purpose. Blier was the incoming president, as the Code launched.
The project addressed a huge need. Art historians, visual artists, art journal and book editors, and museum staff all have faced major hurdles in accomplishing their work because of copyright. Art historians avoided contemporary art in favor of analyzing public domain material. Visual artists hesitated to undertake innovative projects that reuse existing cultural material. Editors, or sometimes their authors, faced monumental bills for permissions and sometimes those permissions depended on an artist or artist’s estate agreeing with what they say. Museums hesitated to do virtual tours, or use images in their informational brochures, or even to mount group exhibits, because of prohibitive permissions costs. All together, some people in the visual arts called this “permissions culture.”
Once the Code came out, some things changed immediately. Museums rewrote their copyright use policies. Artists made new work. CAA’s publications—some of the leading journals in the field—adopted fair use as a default choice.Yale University Press prepared new author guidelines for fair use of images in scholarly art monographs to encourage fair use. Blier was one of the Code’s champions.
And then she needed it herself. As she began work on her most recent book, which ultimately resulted in Picasso’s Demoiselles: The Untold Origins of a Modern Masterpiece (Duke University Press, 2019, winner of the 2020 Robert Motherwell Book prize for an outstanding publication in the history and criticism of modernism in the arts by the Dedalus Foundation), she realized the subject faced the stiffest possible copyright challenge. To tell her story, she would have to be able to show images from a variety of artists, most challengingly, Picasso. She thought of Duke University Press, a publisher that has been willing to go ahead of others on fair use. So Blier approached them. Duke was very supportive, and they ended up hiring extra legal counsel for this. In the end, Blier said, she had to rewrite certain sections, and redo some images at the suggestion of outside counsel, to strengthen the fair use argument.
Blier tells the story of how the book got out into the world (and won an award), below.

Figure 1. Congo masks published in Leo Frobenius’ 1898 Die Masken und Geheimbünde Afrikas alongside Pablo Picasso’s Study of Man (1907). The Congo mask at the bottom, second from the left is the likely source for the crouching demoiselle. The mask at the top left shows tear lines from the eyes crossing diagonally down the cheeks similar to Picasso’s preliminary study for one of the men in an early compositional drawings for the canvas.
You’re an expert in African art. How did you end up writing a book about one of the most famous modernist artists?
This is a book I never intended to write; it found me. For my previous book, Art and Risk in Ancient Yoruba: Ife History, Power, and Identity, I was doing those last-minute bits of work in the library to check sources, and I pulled out a book adjacent to the book I was looking for, an old book by the German anthropologist, Leo Frobenius. I hadn’t read it since graduate school. As I opened it up, I looked down and I said, Wow, this is a book on African masks and they look like they’d be the ones Picasso used as models for his famous 1907 painting Demoiselles d’Avignon. At the time I had first read the book, Picasso’s drawings for the painting hadn’t been released. This time I saw it differently and as I was looking at it in the library, I saw there was tracing paper over the pictures. There was a line drawing covering each mask, and that seemed significant too.
The next thing I knew, I was hunting for a book from the Harvard library on Dahomey women warriors. It turned out it was in the medical school library, which should have been a sign. When I picked it up at the main library and flipped it open, I thought, Oh my god, it’s pornography! It was photos and line drawings of women around the world, in supposed “evolutionary” order. Photos of naked women begin with so-called “archaic,” in Papua New Guinea, right through to southern Europe, then Denmark. In the library I’m bending over, kind of hiding it, out of embarrassment. I bring it home and realize, Ohhhh! Here’s another key source for Demoiselles. This volume, which was by Karl Heinrich Stratz, had gone through multiple editions, and one was published about the same time Picasso stopped using living models. Then I found another book, by Richard Burton, which had a rendering that Picasso clearly used for his 1905 sketch Salomé.
What happened next was the clincher. I went to Paris to lecture at Collège de France. The week before my lectures, I went to hear another speaker at the Collège, a medieval historian. One of the first slides he presented was a work from a medieval illustrator, Villard De Honnecourt. This book was a modern edition of an illustrated medieval manuscript, published in the right time frame for Picasso to have seen it. And I thought, Well, here’s another source Picasso used.
Later I was also able to rediscover a photo that allowed me to date the painting to a single night in March 1907. The scene is often identified as a brothel, but bordel in French doesn’t mean bordello, but rather a chaotic or complex situation. It was my belief that Picasso was creating a time-machine kind of image of the mothers of five races, as he understood them from the Stratz ethno-pornography book and other sources, each depicted in the art style of that region or period. My larger argument is not only that Picasso was using book illustration sources, but also that these books invite us to see the canvas in a new light, and that, for Picasso, the painting has its intellectual grounding in colonial-era ideas about human and artistic evolution.
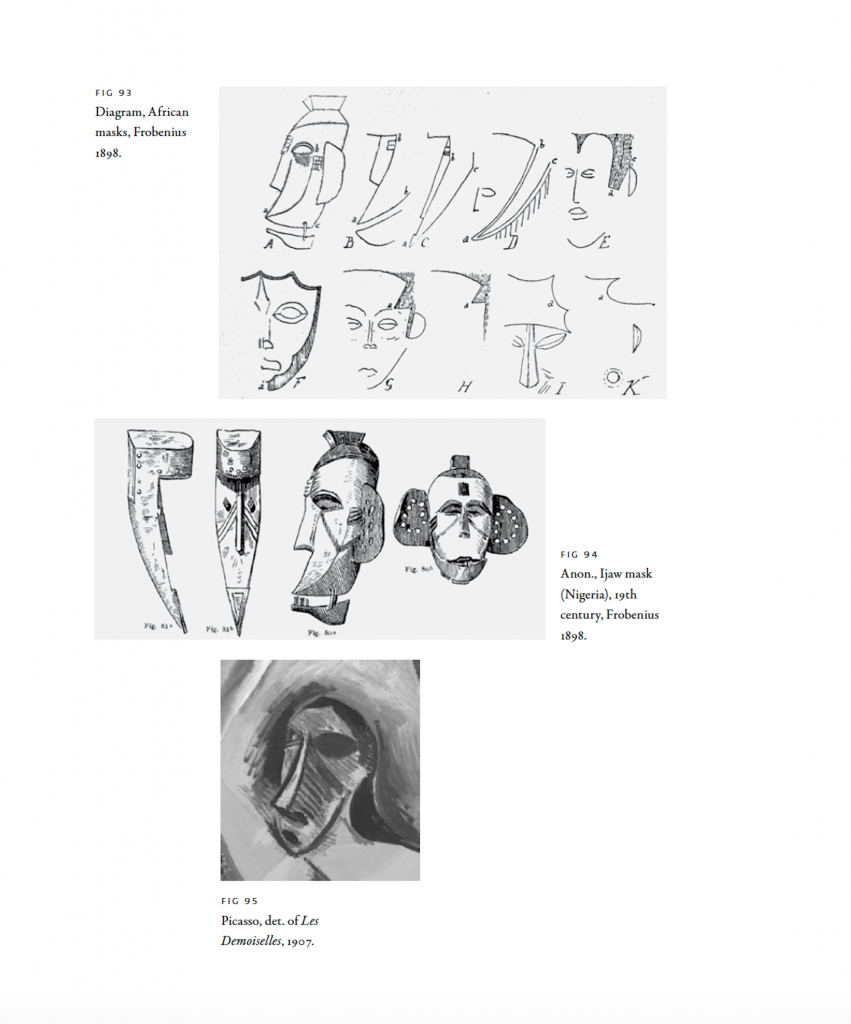
Figure 2. Illustrations from Leo Frobenius’ 1898 Die Masken und Geheimbünde Afrikas showing (top two rows) the visual development of a mask into a human face. The middle illustration ,from the same Frobenius book shows line drawings of ijaw masks from Nigeria. The bottom image is a detail of the standing African figure from Picasso’s 1907, Les Demoiselles d’Avignon which appears to be based on a combination of these two masks.
What a sleuthing job! And so you decided to write the book then?
I wrote the first two chapters while I was in Paris doing the lecture. I saw it not as a coffee-table art book, but the kind of book you put in your knapsack as you head off to a long ride on the subway.
It was easy to write, but it was a very different story for the images. I immediately got a trade publisher in Britain to agree to publish it, and then they said they could not do it, because of problems getting permission to reproduce images from the Picasso Foundation.
The Picasso Foundation is notorious for making it difficult to access Picasso images, isn’t it?
The price of permissions is high, and this Foundation like many estates is interested in guarding the artist’s reputation as well. The difficulties of publishing on Picasso have been manifested in how little publishing was being done, and how scarce the images were in that work. Since 1973, there have been few heavily illustrated books about Picasso, except by wealthy individuals or museums in relation to an exhibition. I had heard about Rosalind Krauss publishing a work without permissions—at least that’s what I heard—anyway, she used very few images. Leo Steinberg apparently had not been able to arrange the rights for a work he wanted to do, a book edition of his two seminal articles on Les Demoiselles.
Although I hadn’t realized it until recently, in September 2019 there was an important case in the US, about a set of illustrated books by Christian Zervos with a wide array of Picasso illustrations. The case was started in France, but a US judge has allowed fair use.
But generally, yes, there’s common wisdom among art historians that the Picasso Foundation is a formidable challenge.
So how did you proceed when the first publisher backed out?
I was disheartened, but I got an agent. He sent it off to ten or twelve trade publishers worldwide—and came up with nothing.
Then I realized I was going to have to go to a university press. That was a big decision. The trade publication will pay for the images, and do all the work on the rights clearance. But with a university press, you’re on your own.
One of the first people I contacted was legendary editor Ken Wissoker at Duke University Press. He was interested, but then came the issue of the images. I may have broached fair use with him from the start. The manuscript had gone through peer review and it was in great shape except for this copyright issue. I had quite a number of images—in the end, it was 338. At Duke, they won’t begin the editorial process until you have all the copyright clearances on images done. So I began the difficult process of deciding how to get the images.
Were you in contact with the Picasso Foundation directly?
I did contact them, in order to let them know about the project in general. I was doing final research work in Paris. I had framed the book as a travelogue in part addressing my discovery of these sources. I also wanted to find out so much more about Picasso. I’m not a modernist, I’m an outsider to the field. So I worked hard to get as much insight and criticism of the manuscript from specialists as I could.
I made it a point to meet with people at the Picasso Foundation. I had a Powerpoint of the images, which I showed to one of the key people there. Later I wrote to them, “here’s the manuscript, let me know if you have any thoughts.” And I heard nothing back. I had heard that with some manuscripts, they have been concerned one way or another. I didn’t want their permission for the intellectual content, but since they knew this artist and his life and family better than any academic could, I wanted their insights.
And then you started to look for permissions?
Well, I began to think about the cost of acquiring the images. The process is such that you have to go through the Artists Rights Society (ARS, a US licensing broker). And to get a price, you have to furnish the number of images, how many are color, the size of the print run, the prospective profit, and a whole series of things we could not know. Duke wouldn’t even look at the project editorially without having the rights in hand. I had heard difficult stories—that they were interested in looking at the galleys along the way, and requesting changes, for quality control, but it wasn’t possible to do this and work with the press.
If I had to guess, I would say that it might have cost me something like $80,000 of my own money to purchase the minimum number of images for this scholarly book, from which I expect to make no money, or very little.

Figure 3 from left to right: Pablo Picasso, Nude Combing Her Hair, 1906; Girl braiding hair from C. H. Stratz, La beauté de la femme, 1900 (Paris); Girl from Vienna from C.H. Stratz, La beauté de la femme, 1900; Picasso Seated Female Nude, 1908. Over the course of his long career Picasso would continue to use key visual insights from Frobenius, Stratz, and other illustrated sources he was exploring in this late 1906 to early 1907 period.
So how did you come to the decision to use them under fair use?
I had been president of CAA in 2016-17, and a longtime promoter of fair use and IP issues more generally. I was involved in the creation of the Code of Best Practices in Fair Use for the Visual Arts. For me, CAA’s role in fair use is one of the most important and radical (in a positive way) things that it has ever done.
I decided that fair use would make the most sense in this context. This was a book about an important modern artist. In addition, I’m a senior scholar—this was not my first publication. If the worst happened, if I had problems, well, I’ve had a great career and this would not harm it. I have tenure and so on. Also, as the then-president of CAA, I thought it was important to do this.
Besides, this to me was part of a larger picture of what I had done in my larger career. I’m very active locally in civic affairs, and really interested in promoting transparency, and democratic ideals. I was also very fortunate to have Peter Jaszi, a foremost legal scholar on fair use (and another principal investigator on the CAA project), working with me. At his suggestion, I took out an insurance policy, which for a fee—I think about $5,000—(with a $10,000 deductible) I was able to lower my anxiety level. I also paid $400 for an attorney to look over the insurance contract. And I had good friends like you, who when I got cold feet assured me it was the right thing to do. And of course, Duke is a publisher that has been willing to go ahead of others on fair use.
Can you give me an example of something you had to change in the text to strengthen the fair use argument?
With a museum photograph of an African mask, for example, I had to explain why this particular way of photographing the work was critical to the argument in my book. I had to ad a few sentences to justify my selection of several Picasso works as well. I also had to give reasons in my text for why each of the chapter epigraphs was necessary.
Did you have to alter the use of imagery in any way to accommodate fair use?
There are changes the press made, design-wise, that reflected in part the decision to employ fair use. Many of the photos are shown in black-and-white and the majority are reduced in size. I was constrained by the fact that I could only employ fair use if I could get access to the materials without going through the Picasso Foundation. So I had to acquire nearly all the images from published books, and many of the Picasso images were published in black and white and at a very small size, in a grainy context. I had to spend a lot of time hunting down the best possible images to use. In my book they are shown in relatively small size, along with information on where you can find color versions online.

That didn’t bother me too much, though. For readers and viewers at this juncture in the Internet era, we have become expert at extrapolating the fuller figure from a small image.
There is also a small spread of color images, a couple Picasso works as well as from other artists. For these images color was central to the book.
The decision to publish largely in black-and-white was, I think, also related to the fact that the Picasso Foundation and others are concerned that color representations be incredibly accurate, and it is very hard to get the color exactly right, when copying from books. You also have an issue with paper quality in getting accurate representation.
The cover is a handsome design, and very clever. They broke up the images into thumbnail-like sections, requiring you as a viewer to put them together as one image, similar to how Picasso was thinking in the early stages of cubism, where you as a viewer of an assemblage have to assemble them in your own mind, to make it work for you as a whole.
How was the book received?
It was a finalist for the Prose Prize, a prize of publishers to authors. My previous book won it in 2016. I didn’t expect to win it this time again, in 2019. I was very honored that it was a finalist. It was also featured in the Wall Street Journal’s holiday art book list. And then, just recently, it won the Robert Motherwell Book Award.
Has the Picasso Foundation seen the book?
To date I’ve heard nothing. I was thinking earlier that the Picasso Foundation might want to stop it pre-publication. So much so that when I came back from travel in Africa, I went first to my academic mailbox, and was relieved when I saw no big legal envelope. But there has been no pushback. I certainly gave them the opportunity to comment on the content while it was still in manuscript. And last April or May, I went to France to meet with the curators at Musée Picasso about contributing an essay to a catalog. I sent them an article draft which they decided not to publish, which is fine, but also sent them a copy of the manuscript, and of course the Musée speaks to the Foundation.
Interestingly, the two cases where the Foundation has sued or prevented publication that I know of have to do with children’s books about Picasso. I don’t know what that means.
Does the wider art history community know about this?
I hope this personal story makes a difference. We still have a lot of educating to do, in spite of the work we did around the Code. I continually get, on the art history listservs, questions—How can I get permission, and I always say, Use fair use. People still don’t trust it or believe it’s more difficult than it is.
At the CAA conference I just went to in Chicago, there seems to be a division between presses. Presses at private universities–Yale, Princeton, MIT, Duke—seem to feel more comfortable exploring this. But for university presses at some public institutions, these legal issues have to be taken up with the state attorney general, and there can be real nervousness stepping outside a narrow parameter. I learned this speaking to an editor at a state university press in a progressive state, who believes they’re being held back because of this fear.
I was pleased to see at this same conference a pamphlet on fair use by Duke University Press’s former Director, Steve Cohn. In his essay, he mentions my Picasso book and how happy he is that Duke chose to publish it this way. I figured, if Steve is openly talking about this fair use project, then the proverbial cat is out of the bag, and I could be more open and provide some of the back story from my end.
CAA’s scholarly publications, The Art Bulletin, Art Journal, and Art Journal Open rely on fair use as a matter of policy, and indicate when they do so in their photo credits. View a complete discussion of fair use and CAA’s Code of Best Practices.
Juan Carlos Rodriguez Rivera and Allison Yasukawa
posted by CAA — December 23, 2019
The weekly CAA Conversations Podcast continues the vibrant discussions initiated at our Annual Conference. Listen in each week as educators explore arts and pedagogy, tackling everything from the day-to-day grind to the big, universal questions of the field.
CAA podcasts are on iTunes. Click here to subscribe.
This week, Juan Carlos Rodriguez Rivera and Allison Yasukawa discuss international and multilingual students at art/design schools.
Juan Carlos Rodríguez Rivera is a queer boricua visual communicator and educator, passionate about food, lover of gradients, and anything with glitter. Juan was born and raised in Cataño, the smallest town of Puerto Rico, but relocated to San Francisco, California in 2017. Juan’s work focuses on challenging colonial perspectives in design from the point of view of a boricua diaspora. Juan Carlos is an Assistant Professor in the Design Department at California College of the Arts, and holds an MFA in Communications Design from Pratt Institute in NY.
Allison Yasukawa is a visual artist and educator. She holds an MFA in Studio Arts and an MA in TESOL and Applied Linguistics. In her studio practice, she explores asymmetries of power and imagined geographies in interactional spaces ranging from the personal to the global. Yasukawa’s pedagogy focuses on studio and academic classes in English for Art and Design. She is the Director of English Language Learning at the California Institute of the Arts and has presented nationally and internationally on art-language overlaps in critique instruction, student autonomy, and multilingualism as a creative resource.
Andrew Demirjian and Claudia Hart
posted by CAA — December 16, 2019
The weekly CAA Conversations Podcast continues the vibrant discussions initiated at our Annual Conference. Listen in each week as educators explore arts and pedagogy, tackling everything from the day-to-day grind to the big, universal questions of the field.
CAA podcasts are on iTunes. Click here to subscribe.
This week, Andrew Demirjian and Claudia Hart discuss emerging media, micro to macro.
Drawing from conceptual art, experimental music and computer science, Andrew Demirjian scrapes and remixes Internet culture to create dense rhythmic collages of sound and language. He teaches theory and production courses in emerging media in the Film and Media Department and the Integrated Media Arts MFA program at Hunter College, he is currently a Fellow at the MIT Open Documentary Lab.
Claudia Hart has been active as an artist, curator and critic since 1988. Her art consists of virtual simulations of all kinds: 3d imagery integrated into photography, multi-channel animation installations, performances, and sculptures using advanced production techniques such as Rapid Prototyping, CNC routing and augmented-reality custom apps. Her works deals with issues of representation, the role of the computer in shifting contemporary values about identity and the real, and ideas about what is usually called the “natural.” Her project is to feminize the masculinist culture of technology by interjecting emotional subjectivity into the overly-determined Cartesian world of digital design.
Kevin Tervala and Jennifer Kingsley
posted by CAA — December 09, 2019
The weekly CAA Conversations Podcast continues the vibrant discussions initiated at our Annual Conference. Listen in each week as educators explore arts and pedagogy, tackling everything from the day-to-day grind to the big, universal questions of the field.
CAA podcasts are on iTunes. Click here to subscribe.
On this week’s podcast, a medievalist stumbles into an Africanist and they decide to invite undergraduates to curate a feminist show.
Correction: Ashton Cooper’s article first appeared as part of a Barnard College exhibition, not Bryn Mawr. For more information: The Problem of the Overlooked Female Artist: An Argument for Enlivening a Stale Model of Discussion
Kevin Tervala is Associate Curator of African Art and Department Head for the Arts of Africa, the Americas, Asia, and the Pacific Islands at The Baltimore Museum of Art.
Jennifer Kingsley is the Director of the interdisciplinary undergraduate Programs in Museums and Society at the Johns Hopkins University.
Pete Schulte and Rubens Ghenov
posted by CAA — December 02, 2019
The weekly CAA Conversations Podcast continues the vibrant discussions initiated at our Annual Conference. Listen in each week as educators explore arts and pedagogy, tackling everything from the day-to-day grind to the big, universal questions of the field.
CAA podcasts are on iTunes. Click here to subscribe.
This week, Pete Schulte and Rubens Ghenov discuss the syncretism that exists between representation and non-objectivity in their current work, the fallacy of binary critiques of art in relation to form and content, as well as the manner in which these interests influence their approach to pedagogy.
Pete Schulte is an artist who lives and works in Birmingham, Alabama. He is Associate Professor of Art and chair of the drawing area at The University of Alabama in Tuscaloosa. Schulte is also co-founder, with artist Amy Pleasant, of The Fuel and Lumber Company curatorial initiative. He recently completed a summer long residency at The Chinati Foundation in Marfa, Texas and will present a solo exhibition of his work at McKenzie Fine Art in New York City later this fall.
Rubens Ghenov was born in São Paulo, Brazil and immigrated to the US in 1989. He lives and works in Knoxville, Tennessee where he is an Assistant Professor of Painting and Drawing at the University of Tennessee. He recently concluded an Affiliated Fellowship at the American Academy in Rome whose works will be in two upcoming group shows, Symbols and Archetypes at Vanderbilt Fine Arts Gallery in Nashville, Tennessee and a yet to be titled show at Mindy Solomon in Miami.
Kristen Lowe and Andrew Wykes
posted by CAA — November 25, 2019
The weekly CAA Conversations Podcast continues the vibrant discussions initiated at our Annual Conference. Listen in each week as educators explore arts and pedagogy, tackling everything from the day-to-day grind to the big, universal questions of the field.
CAA podcasts are on iTunes. Click here to subscribe.
This week, Kristen Lowe and Andrew Wykes discuss living and making in desperate times.
Kristen Lowe is a studio artist, filmmaker, and professor of art and art history at Gustavus Adolphus College. Her studio is located southwest of Minneapolis, Minnesota.
Professor Andrew Wykes teaches at Hamline University in Saint Paul, Minnesota. His teaching career spans 36 years. Andrew is a landscape painter who moved to the United States from the UK in 1995.
Member Spotlight: Barbara Hoffman
posted by CAA — November 21, 2019
Up next in our Member Spotlight series, we are highlighting the work of Barbara Hoffman, founder and principal of The Hoffman Law Firm and a pioneer in the field of art law who served as CAA’s pro bono legal counsel for ten years. Joelle Te Paske, CAA’s media and content manager, spoke with Barbara over the phone to learn about her rich history with CAA. Read the interview, edited for length and clarity, below.

Image courtesy Barbara Hoffman.
Hi Barbara. I’m delighted to have the chance to speak with you. You are one of our esteemed lifetime members who has been a part of the organization in various capacities for more than 40 years. That’s incredible.
The pleasure is mine. I loved working with CAA during my tenure there.
Just looking over your bio on your website, I’m just amazed at how many different roles you’ve taken on over your career as an art lawyer. How did you first get involved with CAA?
I’ve always been interested in art, and I studied in Paris at the Académie Julian during my junior year when I majored in French and Art History. But I wasn’t very aware of the College Art Association.
After my studies, I was one of the early art lawyers. I had founded the Volunteer Lawyers for the Arts in the state of Washington, and continued to develop and write on the subject of art law, at a time when there were only a handful of people who were doing it.
Before then, I practiced civil rights law in New York. I’m from New York—I went to Columbia Law School—and was helping artists on the side when I was in my senior year. I volunteered as a lawyer for the first Volunteer Lawyers for the Arts in New York. I was then recruited to be a law professor in Seattle and I’d had so much fun with Volunteer Lawyers for the Arts that I thought I would join the Washington branch when I moved. When it didn’t exist, I ended up founding the statewide Washington Volunteer Lawyers for the Arts, and hosting an art law clinic at the law school.
Oh, interesting. So it started in New York and then you brought it over to the West Coast, in Washington.
Yes. Then eventually I moved back to New York and I joined the New York City Bar Art Law Committee. I was also Chair of the Public Art Subcommittee. We drafted a balanced, annotated model contract to be made available to artists and administrators. Percent for Art was just starting, and most artists and bureaucrats had little knowledge of copyright and other issues in public art.
The National Endowment for the Arts put together a task force of artists and administrators in which I was invited to participate, alongside Joyce Kozloff, who was on the CAA Board of Directors at the time. Susan Ball was executive director at the time. There was a feminist uprising, and my name was put forward to replace Gil Edelson.
I was CAA’s pro bono outside counsel and member of the executive committee for ten years. Among many activities, I wrote a column for CAA on legal issues. My fondest memories are those of working with the different CAA committees and their chairs. Particularly memorable was the work I did with Albert E. Elsen, a professor of art history and a great scholar on Rodin. We revised the guidelines for the code of ethics for art historians. And I worked with several well-known artists too, many of whom are no longer with us.
I also advised all the CAA publications. This was an interesting time for the issues of fair use and copyright in images. Through me, CAA got involved in what was called the Conference on Fair Use, taking place under the US Patent and Trademark Office and the US Copyright Office, which dealt with bringing copyright law into the digital world.
Before I came in to represent CAA, most of the people there were representing either libraries on one side, who were of course for fair use, or publishers, both trade book and academic publishers, who were of course for a stricter interpretation and enhanced copyright protection. But nobody was really talking about issues like images until we brought up to the subject.
On that issue I worked very hard, and CAA worked very hard. It was extremely controversial for the organization, because as you know, everybody at CAA wears multiple hats and the copyright issues involved both publishers and scholars. So I worked with the Copyright Committee and Fair Use and Christine L. Sundt, president of the Visual Resources Association and a member of CAA. She was a passionate devotee of legal issues there.
I imagine those are the fundamental building blocks for CAA’s Code of Best Practices in Fair Use that was published in 2015.
There are earlier versions of it, too. There was one during my tenure and then it evolved over time. We were never successful in terms of getting the government, the Conference on Fair Use, to be able to come together to develop official guidelines. I spent hours and hours and hours developing scenarios. We tried to get people’s agreement on the analysis and whether it was or wasn’t fair use. But at the end there was never a resolution of that and I think it continued on until 2015. It was a long-going effort. We were the first people to really address the whole issue in the late eighties, early nineties.
That’s fascinating. And especially now, with the emergence of the internet.
Another thing that we were really involved with during my tenure was the issue of freedom of expression. I represented CAA and was active in what we now call the Culture Wars, when Jesse Helms tried to ban the publication of [Robert] Mapplethorpe’s images. This was in 1989, and continued through the 1990s.
They were extremely active times. I’m most proud of the two-volume issue I did on censorship with Robert Storr for Art Journal. It was voted at the hundredth anniversary conference the best Art Journal that was published in the journal’s history.
To accompany this interview, we’ve brought the historic two-volume issue out from behind the paywall for readers to explore through the end of December 2019: Censorship I and Censorship II
For the double issue, I dedicated my statement to Justice Brennan of the Supreme Court. In my view, his decisions on the Supreme Court regarding the First Amendment and freedom of expression basically did more to provide contours of protection for artistic expression than any other Supreme Court Justice.
Then Rob Storr made his editor’s statement a full reprint of Mapplethorpe’s X Portfolio. He got permission from the Mapplethorpe Foundation because of his connections to publish them, but when we sent it to our normal printer, they were afraid to publish it because they thought they (or CAA) would be sued for pornography. They asked us to find a different printer. So we sent it around to all these places that might publish pornography. But the pornography magazines that we sent them to didn’t have the quality that we would require for the CAA journals! So we went to The Burlington Magazine and asked them if they would print it. It was much more expensive, but our usual printer paid the difference. So it was actually printed, by my recollection, by The Burlington Magazine.
There were two fall outs from the issue. The first fall out was a number of CAA members dropped their membership. Pretty amazing. They said the issue should have come with a warning label. You know, they got it in the mail, they left it on the table, and then their children saw it, with no warning.
Another spin off was because the CAA journal goes to every single university that’s a member for the library and art departments, the images that people had been talking about—but never saw—were suddenly available. As part of this I ended up participating in a panel at the University of Nashville, defending a professor who had brought that issue to his class of drawing and photography.
It was all a very meaningful experience. As a result, I was involved in authoring two friends of the court briefs, in the district court and the appellate court, on behalf of the College Art Association. Those were then quoted by the court defending Karen Finley and what they called the NEA Four [Karen Finley, Tim Miller, John Fleck, and Holly Hughes], who had their NEA grants declined because of the Helms amendment. So we introduced a friend of the court brief on behalf of College Art Association, and another one was on behalf of College Art Association and PEN America.
Later on, the organization’s centennial publication featured an image from Faith Ringgold’s French series that I licensed as her lawyer at the time. Faith was an active CAA member on the board and committee on diversity.

CAA’s centennial publication,The Eye, The Hand, the Mind: 100 Years of the College Art Association, with Faith Ringgold’s The Sunflower Quilting Bee at Arles (1996) on the cover.
The complexity of being an art lawyer—it brings you into so many different issues.
It was great. As I said, I worked with all the CAA Committees over that time. I still go to conferences from time to time and participate. And I just, you know, I’m happy to see so many artists that I’ve worked with being rewarded over time by the CAA. I’ve shown up for their presentations, the last ones being Howardena Pindell and Ursula von Rydingsvard for lifetime achievements.
Yes! Our 2019 honorees.
So I’m still keeping up and seeing how the organization has grown and changed. My legacy is these cases, my friends, and the guidelines. A wonderful opportunity for me to combine my passions—law and art history. As a member of the Executive Committee I attended all the CAA annual conferences, and when I wasn’t doing official business, I’d go to art history sessions. I have very happy memories of the wonderful people that I met there. I’m still in contact with many of them. That’s a part of my life that’s ongoing.
That’s wonderful.
And I’m still doing the same thing—still fighting for artists. Still fighting for the first amendment. Still doing public art. So, I feel very fortunate to be a life member.
Barbara Hoffman Biography
The Hoffman Law Firm continues as a preeminent global art and copyright boutique with a focus on Europe, Asia, Africa, and the United States. Author and editor of A Visual Artist’s Guide to Estate Planning (1996 and 2008), Barbara Hoffman also advises artists, galleries, and their estates on legacy planning, and endowed foundations.
Barbara has been recognized by her peers and clients with leadership posts and honor, including as Chair of the New York City Bar Association Committee on Art Law, Chair of the International Bar Association Committee on Art and Cultural Institutions and Heritage Law, and being selected to New York Super Lawyers, Best Lawyers in America, and Best Law Firms in art law and copyright law (2012-2020).
In addition to her service on the CAA executive committee, Barbara serves or has served on many boards, including ArtTable, Performa and the boards of several artists’ foundations. She was voted one of Art and Auction 51’s Power Women in the Art World 2016. www.hoffmanlaw.org
Kerry Hustwit and Megan Griffiths
posted by CAA — November 18, 2019
The weekly CAA Conversations Podcast continues the vibrant discussions initiated at our Annual Conference. Listen in each week as educators explore arts and pedagogy, tackling everything from the day-to-day grind to the big, universal questions of the field.
CAA podcasts are on iTunes. Click here to subscribe.
This week, Kerry Hustwit and Megan Griffiths discuss “Educating the Future Filmmaker: Theory and Practice.”
Kerry Hustwit is a filmmaker and assistant professor of Communication and Digital Media at Neumann University.
Megan Griffiths is an award-winning writer/director working in film and television. She has directed shows for HBO, EPIX, TNT, and Netflix. Additionally, Megan has directed six feature films, among them Eden, which won the Emergent Narrative Director Award and the Audience Award for Narrative Feature at SXSW 2012.








